Have you ever heard of the Content And Pacific Group of States (ACP)? If you haven’t, don’t worry, you’re not alone! The ACP is an organization that many people aren’t familiar with, but it plays a significant role in international cooperation and development. In this article, we’re going to delve into what the ACP is all about and why it’s important. So, buckle up and get ready to learn about this fascinating group!
The ACP is a diverse coalition of 79 countries from Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific. It was established in 1975 with the signing of the Georgetown Agreement in Georgetown, Guyana. The main objective of the ACP is to promote sustainable development and poverty reduction among its member states. These countries have many common challenges, such as limited resources, vulnerabilities to climate change, and a history of colonialism. By working together, the ACP aims to address these issues and improve the well-being of its citizens. In this article, we’ll explore the various programs and initiatives that the ACP has undertaken to achieve its goals. So, get ready to dive deeper into the world of the Content And Pacific Group of States!

Overview of ACP
The African, Caribbean, and Pacific Group of States (ACP) is an international organization consisting of 79 member countries from Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific. The ACP was created with the aim of promoting economic, social, and cultural development among its member states. This article provides an overview of the ACP, its background, objectives, history, structure, trade and economic relations, strategic partnerships, key projects and initiatives, cultural and social aspects, environmental concerns, challenges and opportunities, role in international affairs, importance for member states, critiques and criticisms, future prospects, and a conclusion.
Background of ACP
The ACP was established in 1975 through the signing of the Georgetown Agreement. This agreement brought together former colonies of European powers in Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific, with the purpose of providing a framework for cooperation and development. The ACP was created as a response to the economic and social disparities faced by these regions, and aimed to strengthen their position in the global arena.
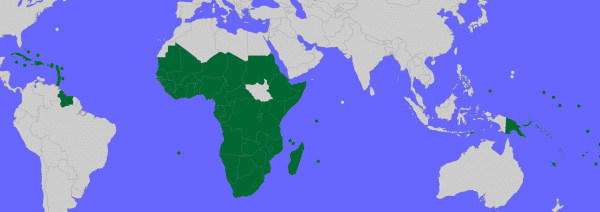
Member States of ACP
The ACP currently consists of 79 member countries, divided into six regions: Africa, the Caribbean, the Pacific, the Indian Ocean, the South Atlantic, and the Indian Ocean. These member states share a common history of colonization and face similar challenges in terms of development and poverty eradication. The diversity of member states allows for a rich exchange of ideas and experiences within the ACP.
Objectives of ACP
The ACP has set forth a number of objectives in order to promote the development and well-being of its member states. These objectives include fostering cooperation among member states, promoting sustainable development, achieving social justice and human rights, promoting peace and security, and strengthening the position of member states in international forums. The ACP aims to achieve these objectives through various programs and initiatives.

History of ACP
Formation of ACP
The ACP was formed in response to the prevailing economic and social disparities among its member states. The former colonies of European powers faced significant challenges in terms of development, and the ACP was created as a platform for addressing these issues collectively. The signing of the Georgetown Agreement marked the formal establishment of the ACP and laid the foundation for its future endeavors.
Evolution of ACP
Over the years, the ACP has evolved to adapt to changing global dynamics and address the emerging challenges faced by its member states. The organization has expanded its activities beyond traditional development cooperation, and now encompasses a wide range of areas such as trade, agriculture, education, and culture. The ACP has also strengthened its engagement with international partners, leading to the formation of strategic partnerships.
Key Events in ACP’s History
Throughout its history, the ACP has witnessed several key events that have shaped its development. These events include the negotiation of various trade agreements with the European Union, the establishment of the ACP Secretariat, the implementation of infrastructure development projects, and the formulation of policies and strategies to address environmental concerns. These milestones reflect the ACP’s commitment to promoting the interests of its member states.
Structure of ACP
Political Structure of ACP
The ACP operates on a three-tier structure comprising the Summit of Heads of State and Government, the Council of Ministers, and the Committee of Ambassadors. The Summit is the highest decision-making body and meets every three years to set the organization’s priorities and policies. The Council of Ministers, composed of foreign ministers, meets annually to discuss and coordinate the implementation of decisions made by the Summit. The Committee of Ambassadors, made up of representatives from member states, meets regularly to monitor the progress of the ACP’s activities.
Decision-Making Process in ACP
The decision-making process within the ACP is characterized by consensus-building and consultation among member states. Decision-making is based on the principles of equality, solidarity, and mutual respect. The ACP seeks to ensure that the concerns and interests of all member states are taken into account when formulating policies and strategies.
Secretariat of ACP
The ACP Secretariat, based in Brussels, serves as the administrative arm of the organization. It is responsible for coordinating and implementing the decisions and policies of the ACP. The Secretariat provides technical support to member states, facilitates negotiations with international partners, and carries out research and analysis on development issues of relevance to the ACP. The Secretariat plays a crucial role in supporting the ACP’s activities and promoting cooperation among member states.

Trade and Economic Relations of ACP
Trade Agreements of ACP
One of the key areas of focus for the ACP is trade and economic cooperation. The ACP has negotiated a series of trade agreements with the European Union, known as the Economic Partnership Agreements (EPAs). These agreements aim to promote the economic development of ACP countries through increased market access, trade liberalization, and development assistance. The EPAs provide a framework for cooperation in a wide range of sectors, including agriculture, fisheries, and services.
Development Assistance for ACP
The ACP recognizes the importance of development assistance in supporting the economic and social development of its member states. The organization works closely with international partners, including the European Union, to mobilize financial resources for development projects and programs. The ACP also advocates for increased Official Development Assistance (ODA) from developed countries, in line with international commitments.
Economic Challenges Faced by ACP
Despite efforts to promote economic development, the ACP faces numerous challenges in this area. Many member states continue to struggle with high levels of poverty, unemployment, and inequality. The ACP is working to address these challenges through targeted initiatives aimed at job creation, entrepreneurship, and investment promotion. The ACP also recognizes the need to enhance the competitiveness of member states’ economies and promote diversification beyond traditional sectors.
Strategic Partnerships of ACP
Relationship with the European Union
The ACP-EU partnership is one of the most important strategic partnerships for the ACP. The partnership is based on a shared history, common values, and mutual interests. Through the Cotonou Agreement, the ACP and the EU have established a framework for political dialogue, development cooperation, and trade relations. The partnership aims to promote sustainable development, poverty eradication, and the integration of ACP countries into the global economy.
Collaborations with other Regional Organizations
In addition to its relationship with the European Union, the ACP actively collaborates with other regional organizations and international partners. The ACP engages with organizations such as the African Union, the Caribbean Community, and the Pacific Islands Forum to promote regional integration, address common challenges, and share best practices. These collaborations enhance the effectiveness of the ACP’s efforts and contribute to the overall development of its member states.
Bilateral Cooperation of ACP
The ACP also engages in bilateral cooperation with individual countries and organizations. Bilateral partnerships allow for targeted interventions and customized approaches to address specific challenges faced by member states. Through bilateral cooperation, the ACP seeks to leverage the expertise, resources, and experiences of its partners to support the development priorities of its member states.

Key Projects and Initiatives of ACP
Infrastructure Development Projects
Infrastructure development is a key focus area for the ACP, as it is vital for economic growth and social development. The ACP implements a range of projects aimed at improving transportation networks, energy infrastructure, and telecommunications systems. These projects help to create jobs, improve access to basic services, and attract investment to member states.
Capacity Building Programs
Capacity building is essential for the sustainable development of ACP countries. The ACP supports capacity building initiatives in areas such as governance, education, health, agriculture, and technology. These programs strengthen the institutional and human resource capacities of member states, enabling them to better address development challenges and seize opportunities.
Sustainable Development Initiatives
The ACP is committed to promoting sustainable development and addressing environmental challenges. The organization implements initiatives aimed at promoting renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, climate change adaptation, and biodiversity conservation. These initiatives contribute to the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and help member states build resilient and sustainable economies.
Cultural and Social Aspects of ACP
Cultural Diversity within ACP
The ACP is characterized by its rich cultural diversity, which is celebrated and promoted through various programs and initiatives. The ACP recognizes the importance of cultural heritage in fostering social cohesion, identity, and creativity. The organization supports cultural exchange, artistic collaborations, and the preservation of cultural traditions within member states.
Social Development Programs of ACP
Social development is a priority for the ACP, as it plays a crucial role in poverty eradication and inclusive growth. The ACP implements programs aimed at improving access to education, healthcare, social protection, and housing. These programs focus on vulnerable groups, including women, children, persons with disabilities, and indigenous peoples.
Education and Training Opportunities
Education and training are essential for the empowerment and employability of individuals in ACP countries. The ACP supports initiatives aimed at improving access to quality education, vocational training, and lifelong learning opportunities. These programs equip individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the job market and contribute to their countries’ development.
Environmental Concerns of ACP
Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation
Climate change poses a significant threat to ACP countries, which are often highly vulnerable to its impacts. The ACP is actively engaged in efforts to adapt to and mitigate climate change. The organization promotes the adoption of climate-resilient practices, the use of clean and renewable energy sources, and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The ACP also advocates for increased financial and technical support for climate action in developing countries.
Natural Resource Management
The sustainable management of natural resources is crucial for the long-term well-being of ACP countries. The ACP supports initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable forest management, responsible fishing practices, and biodiversity conservation. These initiatives contribute to the preservation of ecosystems, the protection of wildlife, and the sustainable use of natural resources.
Conservation Efforts by ACP
Conservation is a key focus area for the ACP, as member states are home to unique and diverse ecosystems. The ACP implements projects and programs aimed at conserving endangered species, protecting natural habitats, and promoting sustainable tourism. These efforts not only contribute to biodiversity conservation but also generate economic opportunities for local communities.
Challenges and Opportunities for ACP
Globalization and its Impact on ACP
Globalization has presented both challenges and opportunities for the ACP. On one hand, globalization has opened up new markets and opportunities for trade and investment. On the other hand, it has exposed ACP countries to increased competition and vulnerability to economic shocks. The ACP is working to ensure that its member states can fully benefit from globalization while addressing the associated risks and challenges.
Emerging Issues for ACP
The ACP faces several emerging issues that require focused attention and innovative solutions. These issues include digital transformation, urbanization, migration, and the impact of new technologies. The ACP is actively exploring ways to harness the potential of these emerging trends for development, while addressing the challenges they pose.
Potential Growth Areas for ACP
Despite the challenges, the ACP has identified several potential growth areas for its member states. These include agriculture, renewable energy, tourism, information and communication technology, and the creative industries. The ACP is working to support these sectors through targeted interventions, capacity building, and promotion of investment and trade.
Role of ACP in International Affairs
Role in Peacekeeping and Conflict Resolution
The ACP plays an important role in peacekeeping and conflict resolution efforts. The organization supports regional initiatives aimed at preventing and resolving conflicts within its member states. The ACP promotes dialogue, mediation, and reconciliation as means to address disputes and promote peace and stability.
Promotion of Human Rights and Democracy
The ACP is committed to upholding human rights, democracy, and the rule of law. The organization advocates for the respect and protection of human rights, including civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights. The ACP also supports initiatives aimed at strengthening democratic institutions, promoting good governance, and fostering civic participation.
Engagement in Global Governance
The ACP actively engages in global governance processes to ensure the voice and interests of its member states are heard and taken into account. The organization participates in international fora such as the United Nations General Assembly, the World Trade Organization, and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. The ACP advocates for the inclusion of developing countries in global decision-making processes and seeks to promote a fair and equitable international order.
Importance of ACP for Member States
Economic Benefits for Member States
Membership in the ACP provides numerous economic benefits for member states. Through trade agreements and development assistance, the ACP supports the economic development of its member states, enhances their competitiveness, and helps to create jobs and improve living standards. The ACP also provides a platform for member states to collectively address economic challenges and leverage their collective strength in negotiations with international partners.
Enhancement of Regional Integration
The ACP contributes to the enhancement of regional integration among its member states. Through regional initiatives and programs, the ACP promotes trade, connectivity, and cooperation among member states within each region. The ACP also supports regional integration efforts in areas such as infrastructure development, energy cooperation, and free movement of people and goods. Regional integration strengthens the economic and political ties among member states and fosters regional stability and development.
Political Influence of ACP
The ACP provides a platform for member states to collectively voice their concerns and interests on the global stage. As a group, the ACP is able to exert political influence and advocate for the needs of its member states. Through its engagement in international affairs, the ACP contributes to shaping global policies and promoting the interests of developing countries.
Critiques and Criticisms of ACP
Effectiveness of ACP’s Policies
The effectiveness of the ACP’s policies and programs has been a subject of debate and criticism. Some argue that the ACP’s development assistance programs have not been able to effectively address the complex challenges faced by member states. Others question the effectiveness of the ACP’s trade agreements in promoting sustainable development and reducing poverty. The ACP continues to review and refine its policies to ensure they are responsive to the needs of member states and deliver tangible results.
Accountability and Transparency Concerns
The ACP has faced criticism regarding its accountability and transparency. Some argue that decision-making processes within the ACP lack transparency and democratic participation. There have also been concerns about the accountability of the ACP Secretariat and the use of financial resources. The ACP recognizes the importance of accountability and transparency and is taking steps to address these concerns through improved governance and reporting mechanisms.
Disparity among Member States
The ACP is composed of countries with diverse levels of development, natural resources, and capacities. This has led to disparities in terms of the benefits and opportunities available to member states. Critics argue that the ACP should do more to address these disparities and promote inclusive growth among its member states. The ACP acknowledges the importance of addressing disparities and is working to ensure that the benefits of its programs and initiatives are distributed equitably among member states.
Future Prospects for ACP
Adaptation to Changing Global Dynamics
The ACP recognizes the need to adapt to changing global dynamics in order to remain relevant and effective. The organization is actively exploring new approaches and strategies to address emerging challenges and opportunities. This includes exploring new partnerships, leveraging technology, and enhancing the organization’s capacity to respond to evolving development priorities.
Reforms and Strengthening of ACP
The ACP is committed to ongoing reforms and strengthening of its structures and processes. The organization is working to streamline its decision-making processes, enhance the effectiveness of its programs and initiatives, and improve the coordination and coherence of its activities. The ACP is also seeking to enhance the participation of member states in the organization’s decision-making processes and activities.
Potential Expansion of ACP
The ACP has the potential to expand its membership and engage with new partners. The organization welcomes new members that share its values and objectives. The ACP also seeks to explore partnerships and collaborations with other like-minded organizations and institutions. The expansion of the ACP’s membership and partnerships would enhance its influence and further strengthen its capacity to address the development priorities of its member states.
Conclusion
The African, Caribbean, and Pacific Group of States (ACP) plays a crucial role in promoting the development and well-being of its member states. Through its diverse programs and initiatives, the ACP addresses a wide range of issues including trade and economic cooperation, infrastructure development, capacity building, cultural and social development, environmental conservation, and international affairs. The ACP’s endeavors are guided by its objectives of fostering cooperation, promoting sustainable development, achieving social justice, and strengthening the position of member states in global forums. As the ACP continues to adapt to changing global dynamics and address emerging challenges, it remains committed to the principles of equality, solidarity, and mutual respect that underpin its efforts.