Have you ever wondered about the economic impact of gold mining in Suriname? Well, get ready to dive into this fascinating topic! In this article, we’ll discuss the various ways in which gold mining has influenced the economy of Suriname. From job creation to foreign investment, you’ll learn all about the significant role that gold mining plays in shaping Suriname’s economic landscape.
Gold mining has long been a major industry in Suriname, and its economic impact cannot be underestimated. The mining sector in Suriname contributes significantly to the country’s GDP, providing a source of revenue that helps fund essential government services and infrastructure projects. Not only does gold mining create employment opportunities for thousands of Surinamese citizens, but it also attracts foreign investors who can contribute to the country’s economic growth. However, as with any industry, there are both positive and negative aspects to consider when examining the economic impact of gold mining in Suriname. Stay tuned to explore the topic further in our in-depth article.

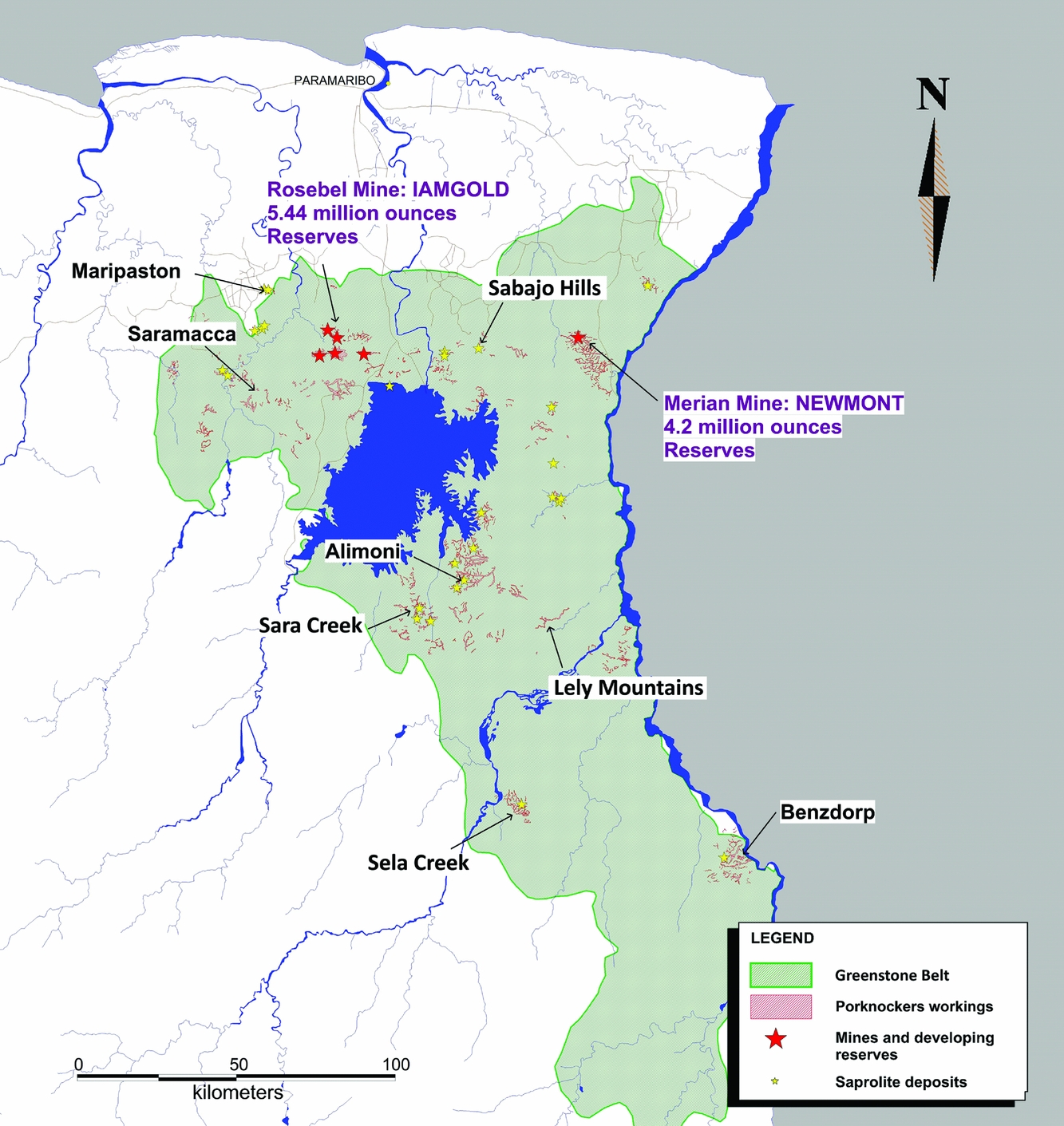
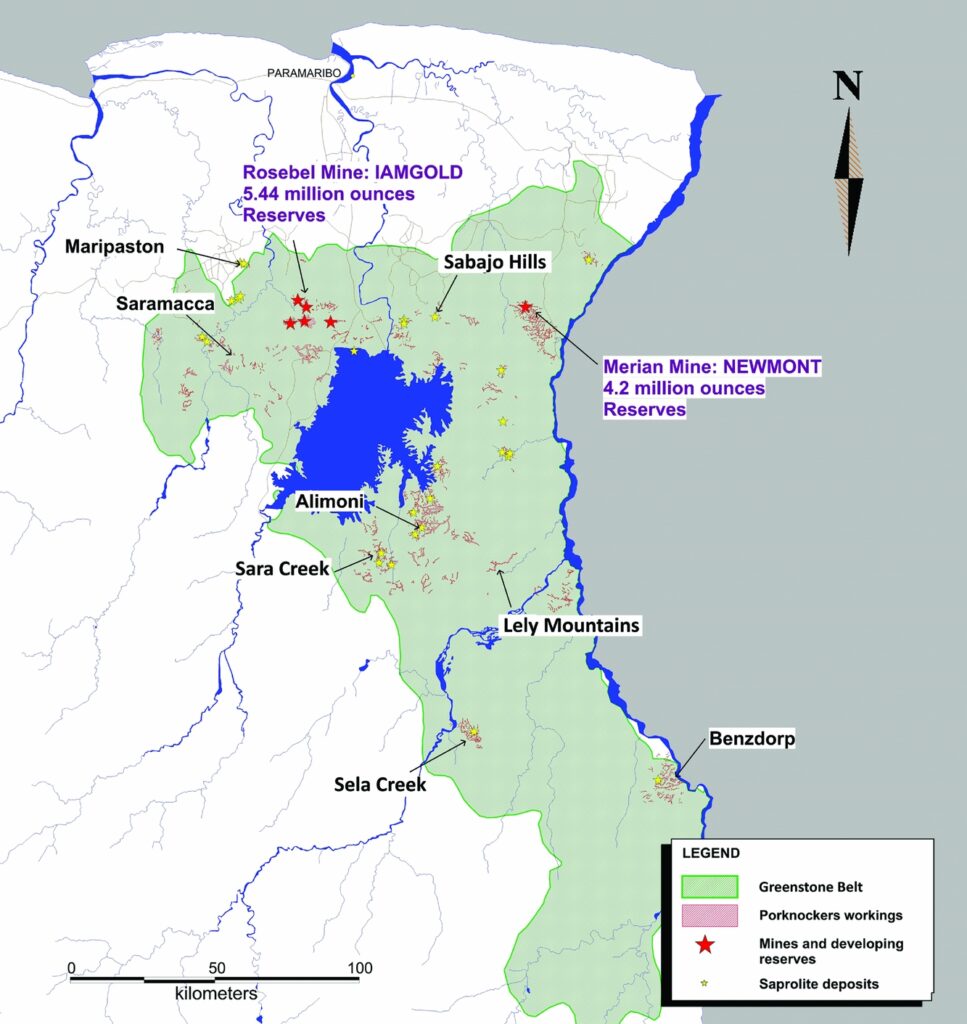
Overview of Gold Mining in Suriname
Suriname, a small country located on the northeastern coast of South America, has a rich history of gold mining. The abundance of gold in its rivers and forests has attracted miners and investors from around the world. In recent years, gold mining has become an important contributor to Suriname’s economy, generating employment opportunities and driving economic growth.
History of Gold Mining in Suriname
Gold mining in Suriname can be traced back to the early 16th century, when European explorers first discovered the precious metal in the country’s rivers. The Dutch colonizers were the first to establish formal mining operations in Suriname, with the establishment of the Berg en Dal and Cassipora mines.
During the colonial period, large-scale gold mining in Suriname was carried out by foreign companies, mainly from the Netherlands. The industry was characterized by the extraction of alluvial gold, which is gold found in the sediments of rivers and streams. This method of mining proved to be profitable, and it led to an influx of workers from neighboring countries to Suriname in search of employment opportunities.

Current State of Gold Mining in Suriname
Today, gold mining in Suriname is a major industry that contributes significantly to the country’s economy. Suriname has the highest per capita gold production in the world, and gold accounts for a significant portion of the country’s total exports.
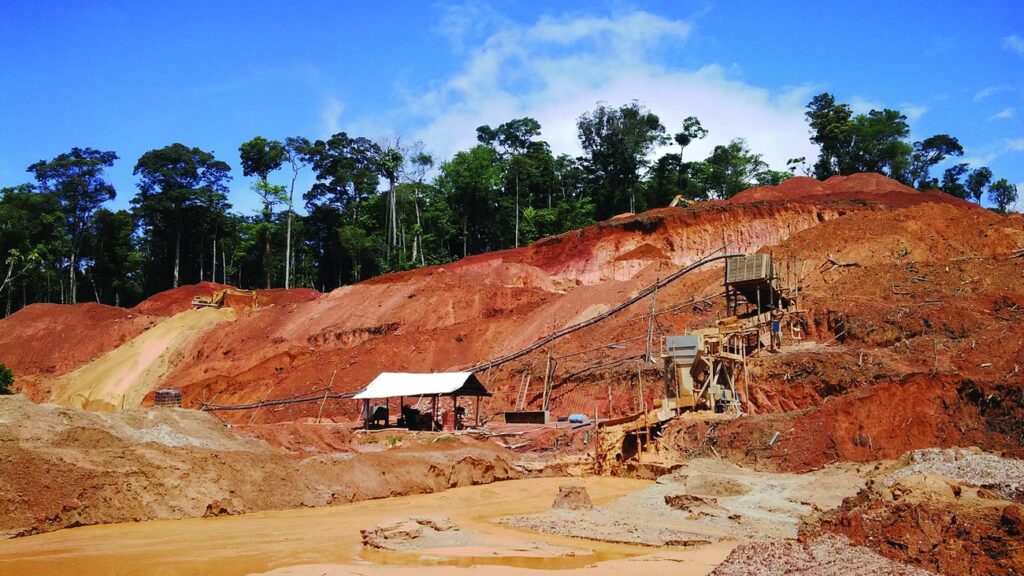
The main method of gold extraction in Suriname is still alluvial mining, although there are also some underground and open-pit mining operations. Alluvial mining involves the use of simple tools such as shovels and pans to extract gold from riverbeds and streams. This method requires minimal capital investment and is accessible to small-scale miners.
Environmental Impact of Gold Mining
While gold mining has brought economic benefits to Suriname, it has also had significant environmental impacts. One of the major concerns is the effect of gold mining on water quality. The use of mercury in the gold extraction process can result in the contamination of rivers and streams, which can have devastating effects on aquatic ecosystems and the health of local communities that rely on these water sources.
Another environmental concern associated with gold mining is deforestation. The clearing of land for mining operations leads to the destruction of forests, which are vital for regulating the climate and providing habitat for numerous species of plants and animals. Deforestation also contributes to soil erosion and increases the risk of flooding and landslides.
Social Implications of Gold Mining
Gold mining in Suriname has both positive and negative social implications. On one hand, it has created employment opportunities for thousands of people, particularly in rural areas where other forms of employment are scarce. Many small-scale miners rely on gold mining as their primary source of income, and the industry has helped alleviate poverty and improve living standards for these individuals.
However, there are also social challenges associated with gold mining. The influx of miners from other parts of Suriname and neighboring countries has led to an increase in population in mining areas, putting pressure on local infrastructure and social services. The presence of informal mining camps has also resulted in social issues such as crime and the spread of diseases.
Employment and Economic Growth
Gold mining in Suriname has been a major source of employment, creating job opportunities for both skilled and unskilled workers. The industry employs thousands of people directly and indirectly, including miners, geologists, engineers, and support staff.
The contribution of gold mining to Suriname’s GDP is significant. Gold exports make up a substantial portion of the country’s total exports, generating foreign exchange earnings and boosting the economy. The revenue generated from gold mining has been used to fund infrastructure development, education, healthcare, and other social programs.

Foreign Investment and Trade
The gold mining industry in Suriname has attracted foreign investment from companies around the world. Foreign companies have brought in capital, expertise, and technology to expand mining operations and improve efficiency.
Suriname’s gold exports have also contributed to international trade. The country exports gold to a variety of destinations, including Europe, North America, and Asia. The revenue generated from gold exports plays a crucial role in balancing the trade deficit and ensuring economic stability.
Government Regulations and Policies
The Surinamese government has implemented laws and regulations to govern the gold mining sector and promote responsible mining practices. The mining code of Suriname sets out the legal framework for mining operations, including the granting of mining concessions, environmental protection measures, and the payment of royalties.
In recent years, the government has placed greater emphasis on sustainable mining practices. It has introduced measures to regulate the use of mercury in gold mining and promote alternatives, such as the use of cyanide and eco-friendly extraction methods. The government has also implemented stricter environmental regulations to minimize the impact of mining on water quality and deforestation.
Infrastructure Development
The growth of the gold mining industry in Suriname has necessitated significant investments in infrastructure. Transportation and logistics are essential for getting mining equipment, supplies, and personnel to remote mining sites. The government has invested in improving road networks and building bridges to facilitate the movement of goods and people.
Power and energy infrastructure is another important aspect of gold mining operations. Suriname has made efforts to expand its electricity grid and improve the reliability of power supply in mining areas. This is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted production and attracting further investment in the mining sector.
Benefits and Challenges for Suriname
Gold mining in Suriname brings both benefits and challenges to the country. On the positive side, it has contributed to economic growth, employment creation, and poverty reduction. The revenue generated from gold exports has been used to fund social programs and infrastructure development, improving the quality of life for Surinamese citizens.
However, there are also challenges related to environmental and social sustainability. Gold mining has had negative impacts on water quality and deforestation, which can have long-term consequences for the environment and local communities. There is a need for sustainable mining practices and stronger regulations to address these challenges and ensure the industry’s long-term viability.
Community Development and Corporate Social Responsibility
Mining companies operating in Suriname have recognized their social responsibility and have implemented community development initiatives. These initiatives aim to improve the livelihoods of local communities, enhance infrastructure, and provide access to education and healthcare.
Corporate social responsibility programs have also been established in the gold mining sector. These programs focus on environmental conservation, health and safety measures for workers, and initiatives to promote local entrepreneurship. Mining companies have partnered with local communities and NGOs to implement these programs and ensure their effectiveness.
Sustainable Mining Practices
Efforts have been made in Suriname to promote sustainable mining practices in the gold mining sector. This includes reducing the use of mercury in gold extraction, implementing reclamation plans to restore mined areas, and promoting responsible waste management.
The Surinamese government and mining companies have also invested in research and development to explore cleaner and more efficient extraction methods. Technological advancements, such as the use of advanced machinery and equipment, have helped improve productivity and reduce the environmental footprint of mining operations.
Future Outlook and Potential Opportunities
The future of gold mining in Suriname looks promising, as there are several potential opportunities for growth and development. Technological advancements in the industry, such as the use of drone technology and advanced exploration techniques, can help identify new gold deposits and improve the efficiency of mining operations.
Diversification of Suriname’s mining industry is another potential opportunity. While gold has been the main focus of mining activities, Suriname also has other mineral resources, such as bauxite, copper, and oil. Diversifying the mining sector can reduce reliance on gold and create a more balanced and resilient economy.
Role of Government in Mining Sector
The Surinamese government plays a crucial role in promoting responsible mining practices and supporting the mining sector. It is responsible for enforcing mining laws and regulations, granting mining concessions, and ensuring compliance with environmental and social standards.
The government has also implemented initiatives to support local businesses and entrepreneurship in the mining sector. It has provided training and capacity-building programs for small-scale miners and encouraged the development of local supply chains. This helps create a more inclusive and sustainable mining industry that benefits Surinamese citizens.
International Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration with international organizations is crucial for promoting sustainable mining practices in Suriname. The government has partnered with organizations such as the United Nations and the World Bank to access technical expertise and financial support for implementing sustainable mining initiatives.
Partnerships with responsible investors are also important for the development of Suriname’s mining industry. These partnerships can provide the necessary capital and expertise to expand mining operations while ensuring social and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
Gold mining has had a significant economic impact in Suriname, driving employment and economic growth. However, it has also had environmental and social implications that need to be addressed. With the implementation of sustainable mining practices, responsible government regulations, and collaboration with international partners, Suriname can maximize the benefits of gold mining while minimizing its negative impacts, ensuring a sustainable future for the industry and the country.