Have you ever wondered about the state of women’s rights in Suriname? Well, let me give you a quick overview of the situation. In Suriname, women have made significant progress in terms of their rights and equality, but there’s still work to be done. In this article, you’ll learn more about the current state of women’s rights in Suriname and the challenges that women still face.
In Suriname, women have gained more opportunities for education and employment, which has contributed to their empowerment and increased their participation in various sectors of society. They have achieved great milestones in areas like politics, where women hold important positions in the government. However, despite these advancements, women in Suriname still face issues such as domestic violence, gender-based discrimination, and limited access to healthcare services. It’s important to understand the complexities of this topic and how it affects the lives of women in Suriname. So, stay tuned to learn more about the challenges and progress of women’s rights in this country. Suriname, a small country located on the northeastern coast of South America, has a complex history when it comes to women’s rights. Throughout the years, the country has made significant progress in promoting gender equality and empowering women, but many challenges still remain. In this article, we will explore the history of women’s rights in Suriname, the legal framework surrounding gender equality, the prevalence of gender-based violence, access to education and healthcare, the role of women in politics and the economy, and the challenges faced by marginalized groups. Let’s delve into the state of women’s rights in Suriname.

History of Women’s Rights in Suriname
Colonial Era
During the colonial era, Suriname was under Dutch rule. Women in the colony were subjected to patriarchal norms and faced significant restrictions on their rights and freedoms. Their roles were largely confined to domestic duties, and they had limited access to education and economic opportunities.
Independence Movement and Early Independence
Suriname gained its independence from the Netherlands in 1975, marking a turning point in the country’s history. The independence movement brought about increased awareness of the need for women’s rights and equality. During this period, women activists began advocating for gender equality and the recognition of women’s rights as fundamental human rights.
Post-Independence Period
In the post-independence period, Suriname made significant strides in promoting women’s rights. Women’s organizations emerged, focusing on issues such as education, economic empowerment, and gender-based violence. However, despite these efforts, women continued to face discrimination and marginalization in various aspects of society.
Legal Framework for Women’s Rights
Constitutional Provisions
Suriname’s Constitution recognizes the equality of all citizens, regardless of gender. It prohibits discrimination on the grounds of sex and guarantees equal rights and opportunities to all individuals. Additionally, it stipulates that the state shall take measures to promote gender equality and ensure the protection of women’s rights.
Gender Equality Legislation
Suriname has enacted several laws aimed at promoting gender equality. The Gender Equality Act, passed in 1986, prohibits discrimination on the basis of sex in various areas, including employment, education, and access to goods and services. The Act also establishes a National Gender Bureau responsible for promoting gender equality and monitoring its implementation.
Domestic Violence Laws
Recognizing the pervasive issue of domestic violence, Suriname has implemented legislation to address this problem. The Domestic Violence Act, enacted in 2009, criminalizes domestic violence and provides measures to protect victims. It also establishes a National Coordinator for Domestic Violence, tasked with coordinating efforts to prevent and respond to domestic violence.
Reproductive Rights
Suriname recognizes reproductive rights as fundamental human rights. Women have the right to make decisions regarding their own bodies, including access to contraception, family planning services, and safe and legal abortion. The country has taken steps to ensure access to reproductive healthcare services, including maternal health services and family planning clinics.

Gender-Based Violence in Suriname
Prevalence and Statistics
Gender-based violence remains a prevalent issue in Suriname. According to a study conducted by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), approximately 40% of women in Suriname have experienced some form of physical or sexual violence in their lifetime.
Forms of Gender-Based Violence
Gender-based violence in Suriname takes various forms, including domestic violence, sexual harassment, rape, and intimate partner violence. Indigenous and Maroon women, in particular, face unique challenges and are disproportionately affected by gender-based violence.
Impact on Women and Society
Gender-based violence has far-reaching effects on women and society as a whole. It not only causes physical and psychological harm to victims but also perpetuates gender inequality and reinforces harmful gender norms. It hinders women’s ability to fully participate in society and limits their opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Efforts to Combat Gender-Based Violence
The Surinamese government and civil society organizations have made efforts to combat gender-based violence. Awareness campaigns, legal reforms, and support services for survivors have been implemented to address this issue. However, more needs to be done to ensure the effective prevention and response to gender-based violence.
Access to Education for Women and Girls
Primary and Secondary Education
Suriname places great importance on education. Girls and boys have equal access to primary and secondary education. The government has implemented measures to promote girls’ education, including scholarships and incentives to encourage their enrollment and retention in schools.
Tertiary Education
Tertiary education is accessible to both women and men in Suriname. Women outnumber men in some tertiary institutions, indicating their increasing participation in higher education. However, gender disparities still exist in certain fields of study, with women being underrepresented in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines.
Gender Disparities in Enrollment and Completion
While access to education is generally equitable, gender disparities still persist in terms of enrollment and completion rates. Cultural norms and gender stereotypes often discourage girls from pursuing certain fields of study or continuing their education. Efforts are being made to address these disparities and promote gender parity in education.
Government Initiatives for Educational Equality
The Surinamese government has implemented initiatives to promote educational equality. This includes the provision of scholarships and grants to students from disadvantaged backgrounds, as well as the establishment of support systems to ensure the retention and success of girls in schools. These efforts aim to break down barriers and create equal opportunities for all students.

Women’s Political Participation
Representation in Government
Women’s representation in Suriname’s government has increased over the years, but they still remain underrepresented in decision-making positions. The country has made progress in terms of women’s political participation, with women holding positions in the National Assembly and the cabinet. However, there is still a need for more women to be involved in politics at all levels.
Electoral Reforms to Enhance Women’s Participation
Suriname has implemented electoral reforms to enhance women’s participation in politics. These reforms include the introduction of quotas, which mandate a minimum percentage of women on candidate lists. Additionally, political parties are encouraged to promote gender diversity in their leadership and candidate selection processes.
Challenges and Progress
Women in politics face various challenges, including societal expectations, limited access to financial resources, and gender biases. Despite these challenges, there have been notable achievements in women’s political participation in Suriname. It is crucial to continue advocating for the inclusion and empowerment of women in decision-making processes.
Women’s Economic Empowerment
Labor Force Participation
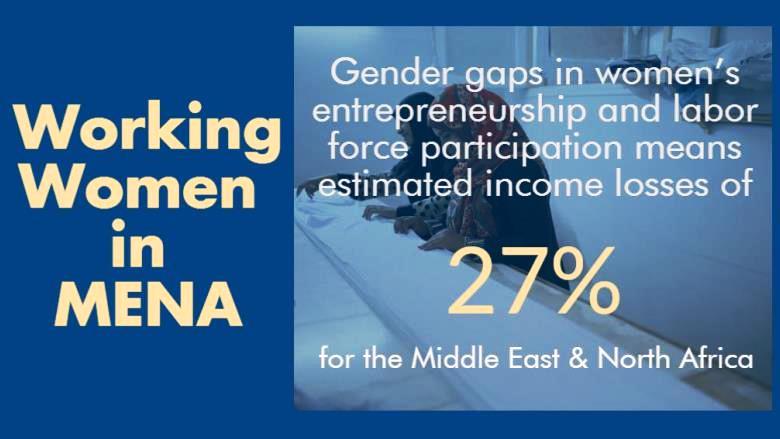
Women in Suriname actively participate in the labor force, contributing to the country’s economy. However, gender disparities persist, with women often being concentrated in low-paying and informal sectors. Women also face challenges such as unequal pay, limited access to career advancement opportunities, and the burden of unpaid care work.
Gender Wage Gap
The gender wage gap remains a significant issue in Suriname. Women tend to earn less than men for equal work or work of equal value. Efforts have been made to address this issue, including the implementation of policies to promote pay equity and equal opportunities for women in the workforce.
Entrepreneurship and Business Ownership
Women in Suriname are increasingly engaging in entrepreneurship and business ownership. The government has implemented programs and initiatives to promote women’s entrepreneurship, including access to financial resources and business development support. However, further efforts are needed to address barriers and create an enabling environment for women entrepreneurs.
Government Policies to Promote Economic Empowerment
The Surinamese government has developed policies and programs to promote women’s economic empowerment. These include initiatives to increase women’s access to credit, training programs to enhance their skills and capabilities, and the establishment of networks and platforms for women-led businesses. These efforts aim to foster an inclusive and vibrant economy that benefits all.
Health and Reproductive Rights
Maternal Health
Suriname has made progress in improving maternal health outcomes. The government has invested in healthcare infrastructure, trained healthcare professionals, and implemented strategies to reduce maternal mortality rates. Efforts are also being made to increase access to prenatal and postnatal care, as well as skilled birth attendants.
Access to Reproductive Healthcare
Suriname recognizes the importance of ensuring access to comprehensive reproductive healthcare services. These services include family planning, antenatal and postnatal care, and sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention and treatment. The government has established clinics and outreach programs to provide these services to women and girls.
Family Planning and Contraception
Family planning services and contraception options are available in Suriname. The government has implemented programs to promote family planning and educate individuals about the importance of reproductive health. However, there is a need for further awareness and accessibility of these services, particularly in remote areas.
Reproductive Rights Advocacy
Civil society organizations in Suriname actively advocate for reproductive rights and the autonomy of women in making decisions about their reproductive health. These organizations work to promote awareness, provide support services, and engage in policy advocacy to ensure the fulfillment of reproductive rights for all women.
Violence Against Indigenous and Maroon Women
Unique Challenges Faced by Indigenous and Maroon Women
Indigenous and Maroon women in Suriname face unique challenges, including land rights violations, discrimination, and marginalization. They often experience higher rates of poverty, limited access to education and healthcare, and higher rates of violence and abuse. It is crucial to address their specific needs and protect their rights.
Indigenous and Maroon Women’s Activism
Indigenous and Maroon women have been at the forefront of activism and advocacy in Suriname. They have organized movements, raised awareness about their rights, and called for greater representation and inclusion. Their efforts have contributed to the recognition of their rights and the implementation of specific policies to address their needs.
Government Initiatives for Indigenous and Maroon Women’s Rights
The Surinamese government has taken steps to promote and protect the rights of indigenous and Maroon women. It has recognized their land rights, established mechanisms for their representation and participation, and implemented programs to address their specific needs. However, more needs to be done to address the underlying issues they face.

The Role of NGOs and Civil Society
Prominent Women’s Rights Organizations
Several prominent women’s rights organizations operate in Suriname, working towards the advancement of gender equality and the promotion of women’s rights. These organizations provide support services, conduct research and advocacy, and collaborate with the government and international organizations to address gender inequalities.
Advocacy and Support Services
Women’s rights organizations in Suriname play a crucial role in advocating for policy reforms, raising awareness about women’s rights issues, and providing support services to survivors of gender-based violence. They offer shelter, counseling, legal assistance, and empowerment programs, and work to create a safe and inclusive environment for women and girls.
Collaboration with Government and International Organizations
Women’s rights organizations in Suriname collaborate with the government, international organizations, and other civil society actors to address women’s rights issues. They participate in policy dialogues, contribute to the development of legislation, and work towards the implementation and monitoring of international commitments on gender equality.
Media Representation of Women
Portrayal in Entertainment Media
The representation of women in entertainment media in Suriname has improved over the years, with more female voices and stories being featured. However, gender stereotypes and traditional gender roles still persist in some media portrayals. Efforts are being made to promote diverse and positive representations of women in the media.
Representation in Journalism and News
Women in Suriname have made significant strides in the field of journalism, with many women working as reporters, anchors, and editors. However, gender biases and stereotypes still exist, affecting the representation of women’s perspectives and experiences in news coverage. Promoting gender-sensitive journalism and increasing the representation of women in decision-making positions within media organizations is crucial.
Media’s Influence on Gender Norms
The media plays a significant role in shaping societal perceptions of gender norms in Suriname. It has the power to challenge and reinforce traditional gender roles and stereotypes. It is essential for the media to promote gender equality, challenge harmful norms, and ensure diverse and inclusive representation of women in all aspects of media content.
Challenges and Discrimination Faced by LGBTQ+ Women
Legal Recognition and Protection
Suriname has made progress in legal recognition and protection for LGBTQ+ individuals. Same-sex sexual activity is decriminalized, and a constitutional amendment in 2020 prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation. However, challenges remain in fully recognizing and protecting the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals, including transgender rights and same-sex marriage.
Social Stigma and Discrimination
Social stigma and discrimination continue to affect LGBTQ+ individuals in Suriname, including LGBTQ+ women. Homophobic and transphobic attitudes persist in society, leading to exclusion, harassment, and violence. It is crucial to challenge these prejudices and work towards creating an inclusive and accepting society for all individuals, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity.
LGBTQ+ Activism and Support Networks
LGBTQ+ activism and support networks have emerged in Suriname, advocating for the rights and wellbeing of LGBTQ+ individuals. These organizations provide support services, raise awareness, and engage in advocacy for legal reforms and policy changes. Their efforts have contributed to greater visibility, acceptance, and recognition of LGBTQ+ rights in Suriname.
Intersectionality and Women’s Rights
Impact of Intersectionality on Women’s Rights
Intersectionality refers to the interconnected nature of social identities, such as gender, race, class, and ethnicity, and how they intersect to shape individual experiences. In Suriname, women’s experiences and access to rights are influenced by various intersecting factors. Addressing intersectionality is crucial to ensure the rights and wellbeing of all women, particularly those from marginalized groups.
Experience of Marginalized Women
Marginalized women in Suriname, including indigenous and Maroon women, women with disabilities, and women from low-income backgrounds, face multiple forms of discrimination and exclusion. They often experience compounded barriers in accessing education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Their experiences highlight the need for an inclusive and intersectional approach to women’s rights.
Inclusive Feminist Movements in Suriname
Feminist movements in Suriname have increasingly embraced intersectionality and the inclusion of marginalized voices. These movements work towards dismantling systems of oppression and promoting gender equality for all women. By recognizing and addressing the unique challenges faced by different groups of women, inclusive feminist movements contribute to a more comprehensive and effective women’s rights agenda.
International Commitments and Progress
Suriname’s Ratification of International Conventions
Suriname has ratified various international conventions and treaties that promote and protect women’s rights, including the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) and the Beijing Platform for Action. By ratifying these conventions, Suriname has committed to upholding the principles of gender equality and non-discrimination.
Implementation and Compliance with Obligations
Suriname has taken steps to implement its international obligations regarding women’s rights. This includes the development and implementation of national action plans, gender mainstreaming strategies, and the establishment of institutions responsible for the promotion and monitoring of women’s rights. However, challenges remain in fully complying with these obligations.
International Support and Cooperation
International organizations and donor agencies provide support to Suriname in advancing women’s rights. They offer technical assistance, capacity-building programs, and funding to strengthen the government’s efforts in promoting gender equality. International cooperation is crucial in addressing the systemic challenges faced by women in Suriname and ensuring the fulfillment of their rights.
Conclusion
Significant progress has been made in promoting women’s rights in Suriname, but challenges and inequalities persist. The country has established a legal framework for gender equality, implemented policies to address gender-based violence, increased access to education and healthcare, and taken steps to promote women’s political and economic empowerment. However, women in Suriname still face discrimination, gender-based violence, and barriers to full realization of their rights.
Addressing the remaining challenges requires sustained efforts from the government, civil society organizations, and international partners. It is crucial to continue advocating for the rights of marginalized groups, promote intersectionality in women’s rights discourse, challenge harmful gender norms, and foster inclusive and supportive environments for all women.
By working together and ensuring the full participation and empowerment of women, Suriname can create a society where gender equality is not just a concept, but a lived reality for all.